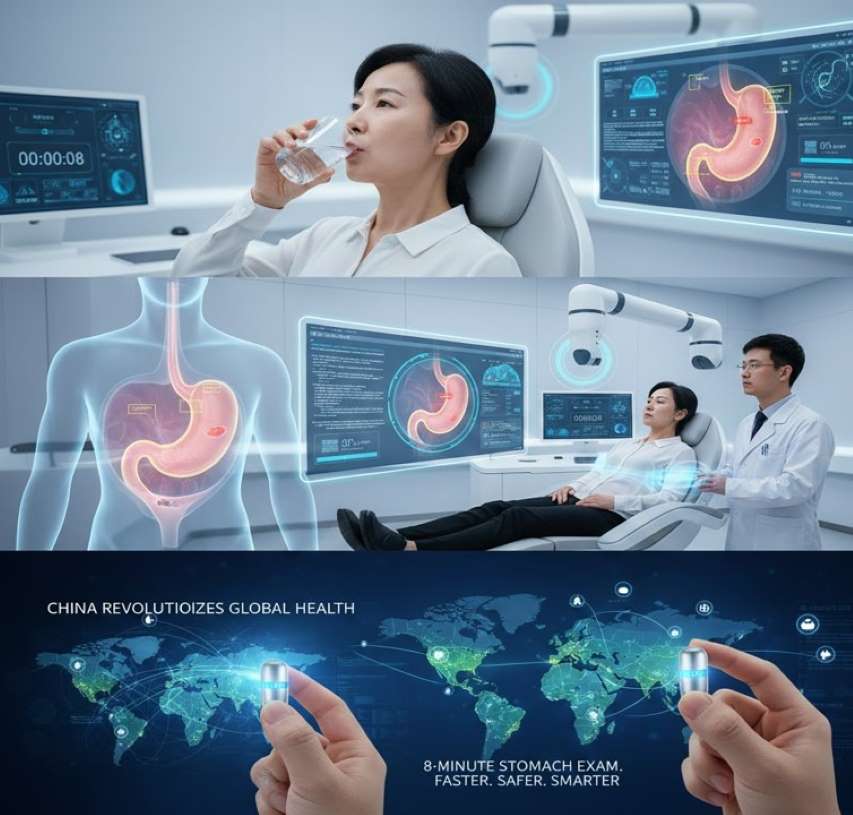
In a groundbreaking advancement in medical technology, Chinese researchers and companies have developed an innovative Artificial Intelligence-powered smart capsule that promises to transform the diagnosis of stomach problems. This tiny, swallowable device can perform a comprehensive stomach examination in as little as eight minutes, eliminating the need for invasive procedures like traditional endoscopy. With no tubes, no anesthesia, and minimal discomfort, this technology is already making waves in the healthcare system of China and could soon redefine global digestive health diagnostics.
A Leap Forward in Non-Invasive Diagnostics
The device, known as the Fully Automated Magnetically Controlled Capsule Endoscopy, represents the culmination of over a decade of research and development in magnetically guided capsule endoscopy. Initial concepts for magnetically controlled capsules date back to the early 2010s, with early prototypes tested in models, animals, and human volunteers.
China quickly became a leader in this field, with companies such as Ankon Technologies and Jinshan Technologies introducing advanced systems between 2012 and 2014. Jinshan further advanced the technology in 2019 by incorporating full automation and Artificial Intelligence integration. Today, these systems are in clinical use across Chinese hospitals, proving their safety and efficacy through rigorous real-world applications.
How the Smart Capsule Works
The process is remarkably simple and patient-friendly. The procedure involves a few straightforward steps:
Ingestion: Patients swallow the small capsule—measuring approximately 11 to 27 millimeters in length—with a sip of water.
Magnetic Guidance: Once inside the stomach, the capsule is guided externally by magnetic fields generated by a robotic arm. This allows for precise maneuvering, including tilting and rotating to navigate through gastric folds.
High-Resolution Imaging: Equipped with advanced image sensors, the capsule captures real-time images and transmits them wirelessly to dual monitors.
Artificial Intelligence Analysis: AI algorithms analyze the footage on the spot to detect abnormalities and identify anatomical landmarks with 80% to 90% accuracy.
In fully automated mode, the robot completes a gastric scan in approximately eight to fifteen minutes. Recent iterations have reduced the time for a full stomach check to just eight minutes.
Key Benefits and Advantages
The primary appeal of the smart capsule is its non-invasive nature. Unlike conventional gastroscopy, which involves inserting a tube through the mouth and often requires sedation, this method causes no discomfort and carries a low risk of infection because the device is disposable.
High Acceptability: Studies show excellent patient tolerance, making it ideal for the elderly or those who cannot undergo traditional endoscopy.
Efficiency: Artificial Intelligence integration reduces image reading time from 25 minutes to mere moments, allowing physicians to handle more cases.
Comprehensive Detection: The capsule excels at spotting ulcers, bleeding, inflammation, polyps, and early signs of gastric cancer.
Technical Specifications and Limitations
The capsule features a battery life of 8 to 16 hours, which is more than enough for a full gastrointestinal exam. It utilizes adaptive frame rates to optimize image quality while conserving power.
However, some limitations remain. The technology may not fully examine the esophagus, and mucus can occasionally obscure the lens. Additionally, while the technology is flourishing in China, high initial costs and the need for interdisciplinary collaboration between engineers and medical experts are ongoing hurdles for global expansion.
Future Implications and Global Potential
As of late 2025, this technology is being hailed as the future of medical diagnostics. Experts predict that these smart capsules could expand globally, particularly in regions with high rates of gastric cancer. By making screenings faster, safer, and more accessible, this innovation could save countless lives through early detection, potentially making the eight-minute stomach check a worldwide standard.
 |  |  |
 |  |  |