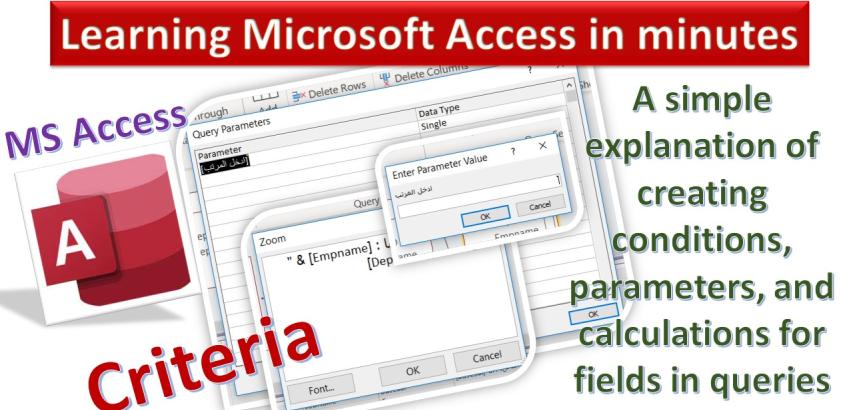
Microsoft Access is a powerful database management system that allows users to create and manipulate databases with ease. One of its key features is the ability to filter and sort data in queries using criteria and parameters. This tutorial will explain how to utilize criteria and query parameters in MS Access to refine and customize your query results.
Calculated Field: A calculated field in MS Access is a field that you create in a query to perform mathematical operations on existing fields. You can use this feature to generate new data based on the values of other fields in your database. This can be especially useful when you need to compute values or derive insights from your data.
Zoom: The Zoom feature in MS Access allows you to create or modify calculated fields more effectively. By right-clicking on a calculated field in the query design grid and selecting "Zoom," you can access an enlarged view where you can enter or edit your calculations with greater visibility and precision.
Calculated Field Caption: When you create a calculated field in a query, you can assign a custom caption to it, making your query results more reader-friendly. This means that you can provide a descriptive label for the calculated field to make it easier for others to understand the purpose of that field.
Fields Concatenation: Concatenation in MS Access refers to the process of combining two or more fields into a single field. You can use the ampersand (&) operator to concatenate text fields and create meaningful combinations of data. For example, you can concatenate a first name and a last name field to display a full name in your query results.
Criteria: Criteria are the conditions you set in your query to filter data based on specific requirements. For instance, you can specify that you want to retrieve only the records where the "Salary" field is greater than 5000. Criteria help you narrow down your results to include only the data that meets your defined conditions.
Criteria Or: When using the "Or" operator in criteria, it means that any one of the conditions you set must be met for a record to be included in the query results. This allows for a more flexible approach, where data that satisfies any of the specified conditions will be displayed.
Criteria And: On the other hand, the "And" operator in criteria requires that all of the conditions must be met for a record to be included in the query results. This approach is more restrictive, as it ensures that records meeting all the specified conditions are shown.
Parameters: Parameters are placeholders that allow you to prompt users for input when running a query. Instead of defining specific criteria, you can use parameters to dynamically gather values from users at runtime. This feature is especially helpful when you want to create queries that can adapt to different input without having to modify the query design every time.
By incorporating these elements into your MS Access database management, you can effectively filter and customize your query results to meet your specific data analysis needs, and allow for more dynamic and interactive queries through the use of parameters.